Apache Druid is an open source database that special built for business intelligence queries (OLPA) on large event dataset. It can provide a very low latency data ingestion, flexible data exploration, and fast data aggregation.
Apache Druid
Druid is written in Java and born in 2011. It’s design is inspired by having a combination of data warehouses, timeseries databases, and logsearch systems.
Key Features
- Data store in columnar format.
- Scalability - Druid can scale horizontally by adding more server.
- Parallelism - Query processed in Druid is running parallelly in the cluster.
- Self healing - When a server is added / remove from the cluster, Druid will handle the rebalancing automatically.
- Time-based partitioning - Druid partition data by time to speed up time series queries.
You should not use Druid when,
- you need low latency when updating record in Druid.
- the reporting system is offline and query latency is not the priority.
- you have to perform many
JOINoperation Druid. This kind of operation require long time to process.
Considering use Druid when,
- Target latency between 100ms - few seconds.
- Update operation is less common.
- Dealing with time series queries.
Running in Local
Druid provide a very complete quickstart guide for running Druid in local. Click here if you only need to run Druid in local machine.
Running in Kubernetes
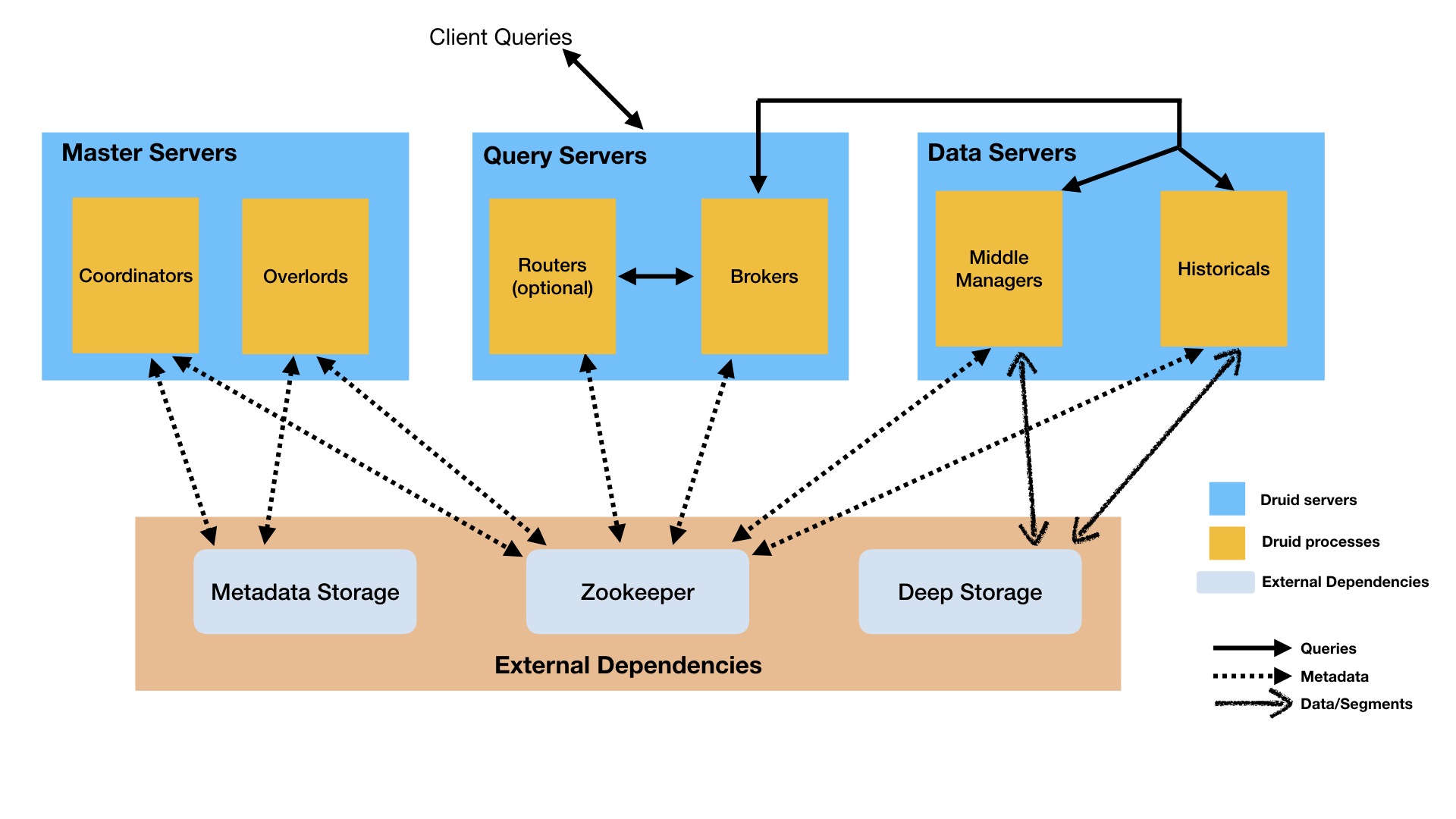
In this section, we will learn how to run Druid in Kubernetes environment. Before going into detail on provisioning Druid cluster in Kubernetes, let’s look into the component/nodes that consist in Druid.
-
Broker
This is the nodes that application/client interact with to obtain data. These nodes aware of where the data lies in the cluster.
-
Coordinator
These nodes manage the data operation (data load, drop, load-balance) on the historical node.
-
Overlord
This node handle the task management and maintain task queue that consist of user submitted task in Druid cluster.
-
Router
These node will route request to Brokers, Coordinators, and Overlords. (Optional)
-
Historical
These nodes will serve queries over immutable data. Historical nodes downloads Druid segment from deep storage and load them into available memory. The status of segment (loaded / should be remove) is tracked and share among other node via Zookeeper.
-
Middle Manager
These nodes responsible for running tasks related to data ingestion, realtime indexing, and segment archives.
Besides of internal component that listed above, Druid also required three external dependencies.
-
Deep Storage
Deep storage is a shared file storage which typically is a distributed object store like S3 or HDFS. Every data ingested into Druid will be store deep storage to serve as a backup. Druid will automatically restore the data from deep storage if it detect any data failure. In this blog post, we will be using S3 as the deep storage.
-
Metadata Store
Metadata storage is required to store metadata which essential for Druid cluster to work.
-
Zookeeper
Druid leverage Apache Zookeeper(ZK) to manage the cluster state such as internal service discovery, coordination, and leader election.
(image source)
Druid Operator
Druid packaged the cluster into an operator Kubernetes application. In this example we will be using Druid operator to install the cluster.
-
Clone the druid operator GitHub repository.
1
git clone git@github.com:druid-io/druid-operator.git
-
Go to the helm chart directory
1
cd druid-operator/chart
-
Install Druid Operator using Helm.
1 2
helm install druid-operator . -n druid-operator \ --create-namespace --set env.DENY_LIST="kube-system"
To uninstall Druid operator.
1
helm uninstall druid-operator -n druid-operator
Postgres DB
By default Druid use Derby to store but it is not recommended for production use. Thus, in this example we will be utilizing Postgres DB to act as the metadata store. (Alternate choice would be MySQL)
In this example, we will provision a Postgres database using helm chart created by Bitnami.
1
helm install my-release --set postgresqlPassword=password bitnami/postgresql
Note:
- db user name =
postgres - db password =
password
Zookeeper
We will be re-using the sample ZK Kubernetes spec in Druid Operator.
1
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/druid-io/druid-operator/master/examples/tiny-cluster-zk.yaml
Druid Cluster
Once Druid operator, Postgres database and Zookeeper is up then we are ready to provision Druid cluster.
durid.yaml - link
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
apiVersion: "druid.apache.org/v1alpha1"
kind: "Druid"
metadata:
name: druid-cluster
spec:
image: apache/druid:0.21.1
# Optionally specify image for all nodes. Can be specify on nodes also
# imagePullSecrets:
# - name: tutu
startScript: /druid.sh
podLabels:
environment: stage
release: alpha
podAnnotations:
dummykey: dummyval
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /status/health
port: 8088
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 1000
services:
- spec:
type: ClusterIP
clusterIP: None
commonConfigMountPath: "/opt/druid/conf/druid/cluster/_common"
jvm.options: |-
-server
-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=10240g
-Duser.timezone=UTC
-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
-Dlog4j.debug
-Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.logging.log4j.jul.LogManager
-Djava.io.tmpdir=/druid/data
log4j.config: |-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Configuration status="WARN">
<Appenders>
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{ISO8601} %p [%t] %c - %m%n"/>
</Console>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Root level="info">
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>
common.runtime.properties: |
# Zookeeper
druid.zk.service.host=tiny-cluster-zk
druid.zk.paths.base=/druid
druid.zk.service.compress=false
# Metadata Store
#druid.metadata.storage.type=derby
#druid.metadata.storage.connector.connectURI=jdbc:derby://localhost:1527//druid/data/derbydb/metadata.db;create=true
#druid.metadata.storage.connector.host=localhost
#druid.metadata.storage.connector.port=1527
#druid.metadata.storage.connector.createTables=true
druid.metadata.storage.type=postgresql
druid.metadata.storage.connector.connectURI=jdbc:postgresql://my-release-postgresql:5432/druid
druid.metadata.storage.connector.host=my-release-postgresql
druid.metadata.storage.connector.port=5432
druid.metadata.storage.connector.createTables=true
druid.metadata.storage.connector.user=postgres
druid.metadata.storage.connector.password=password
# Deep Storage
druid.storage.type=s3
druid.storage.bucket=test-druid-1
druid.storage.baseKey=druid/segments
#
# Extensions
#
druid.extensions.loadList=["druid-kafka-indexing-service", "druid-s3-extensions", "postgresql-metadata-storage"]
#
# Service discovery
#
druid.selectors.indexing.serviceName=druid/overlord
druid.selectors.coordinator.serviceName=druid/coordinator
druid.indexer.logs.type=s3
druid.indexer.logs.s3Bucket=<s3 bucket>
druid.indexer.logs.s3Prefix=druid/indexing-logs
druid.segmentCache.locations=[{"path":"/druid/data/segment-cache","maxSize":10737418240}]
druid.indexer.logs.directory=/druid/data/indexing-logs
druid.lookup.enableLookupSyncOnStartup=false
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /druid/data
name: data-volume
volumes:
- name: data-volume
emptyDir: {}
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: AWS_REGION
value: < Key in your AWS S3 bucket location >
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: < Key in your AWS ACCESS KEY here >
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: < Key in your AWS SECRET KEY here >
nodes:
brokers:
# Optionally specify for running broker as Deployment
# kind: Deployment
nodeType: "broker"
# Optionally specify for broker nodes
# imagePullSecrets:
# - name: tutu
druid.port: 8088
nodeConfigMountPath: "/opt/druid/conf/druid/cluster/query/broker"
replicas: 1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
runtime.properties: |
druid.service=druid/broker
# HTTP server threads
druid.broker.http.numConnections=50
druid.server.http.numThreads=60
# Processing threads and buffers
druid.processing.buffer.sizeBytes=500MiB
druid.processing.numMergeBuffers=4
druid.processing.numThreads=1
druid.sql.enable=true
druid.server.http.defaultQueryTimeout=3000000
extra.jvm.options: |-
-Xmx2G
-Xms2G
coordinators:
# Optionally specify for running coordinator as Deployment
# kind: Deployment
nodeType: "coordinator"
druid.port: 8088
nodeConfigMountPath: "/opt/druid/conf/druid/cluster/master/coordinator-overlord"
replicas: 1
runtime.properties: |
druid.service=druid/coordinator
# HTTP server threads
druid.coordinator.startDelay=PT30S
druid.coordinator.period=PT30S
# Configure this coordinator to also run as Overlord
druid.coordinator.asOverlord.enabled=true
druid.coordinator.asOverlord.overlordService=druid/overlord
druid.indexer.queue.startDelay=PT30S
druid.indexer.runner.type=local
extra.jvm.options: |-
-Xmx512M
-Xms512M
historicals:
nodeType: "historical"
druid.port: 8088
nodeConfigMountPath: "/opt/druid/conf/druid/cluster/data/historical"
replicas: 1
runtime.properties: |
druid.service=druid/historical
druid.server.http.numThreads=5
druid.processing.buffer.sizeBytes=536870912
druid.processing.numMergeBuffers=1
druid.processing.numThreads=1
druid.historical.cache.useCache=true
druid.historical.cache.populateCache=true
druid.server.http.defaultQueryTimeout=3000000
# Segment storage
druid.segmentCache.locations=[{\"path\":\"/druid/data/segment-cache\",\"maxSize\":100737418240}]
druid.server.maxSize=100737418240
extra.jvm.options: |-
-Xmx512M
-Xms512M
routers:
nodeType: "router"
druid.port: 8088
nodeConfigMountPath: "/opt/druid/conf/druid/cluster/query/router"
replicas: 1
runtime.properties: |
druid.service=druid/router
# HTTP proxy
druid.router.http.numConnections=10
druid.router.http.readTimeout=PT5M
druid.router.http.numMaxThreads=10
druid.server.http.numThreads=10
# Service discovery
druid.router.defaultBrokerServiceName=druid/broker
druid.router.coordinatorServiceName=druid/coordinator
# Management proxy to coordinator / overlord: required for unified web console.
druid.router.managementProxy.enabled=true
extra.jvm.options: |-
-Xmx512M
-Xms512M
Note:
- Key in your AWS credential
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY. - Key in your S3 bucket name and location name.
Use the command below to create Durid cluster.
1
kubectl apply -f druid.yaml
Load Data
If the cluster is running in Kubernetes, you will need to port-forward the router service out for interacting with Druid cluster.
1
kubectl port-forward service/druid-druid-cluster-routers 8888:8088
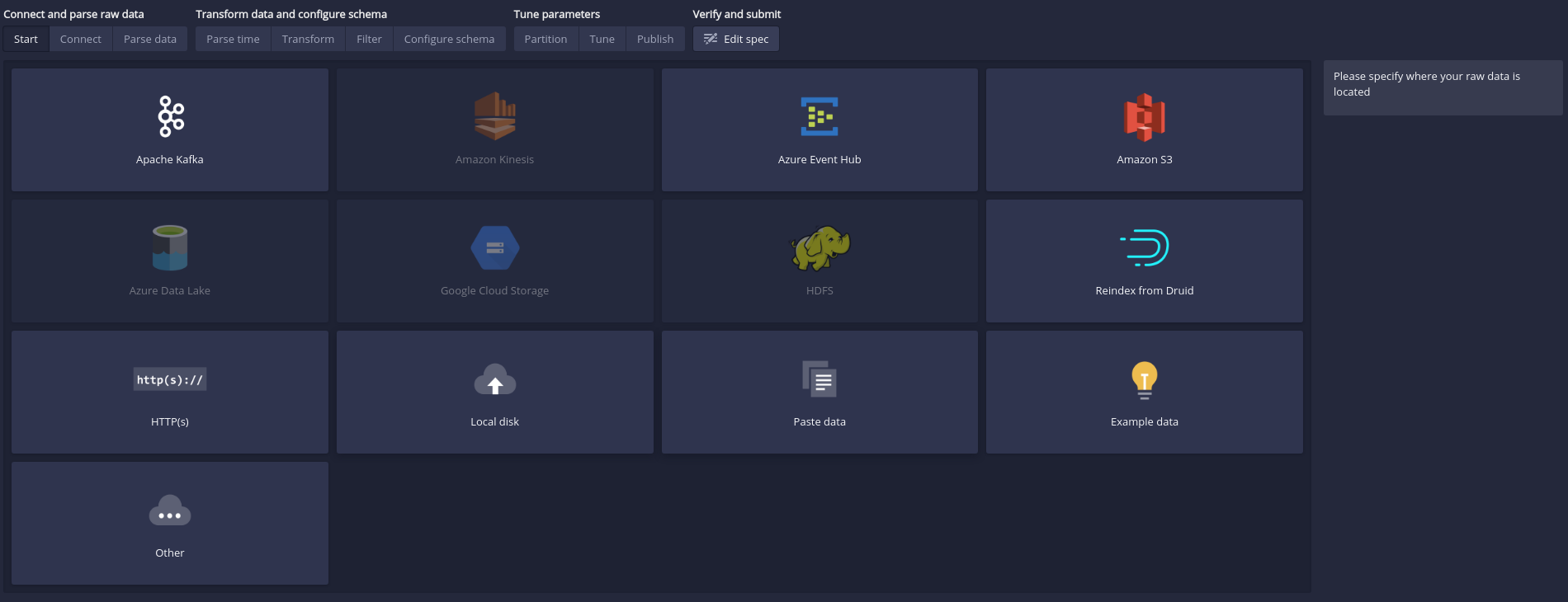
To load data into Druid, we can done it via Web UI or API call.
Web UI
-
Go to http://localhost:8888/
-
Click “Load Data” on the menu.
-
Select the method you want to use to load data.
-
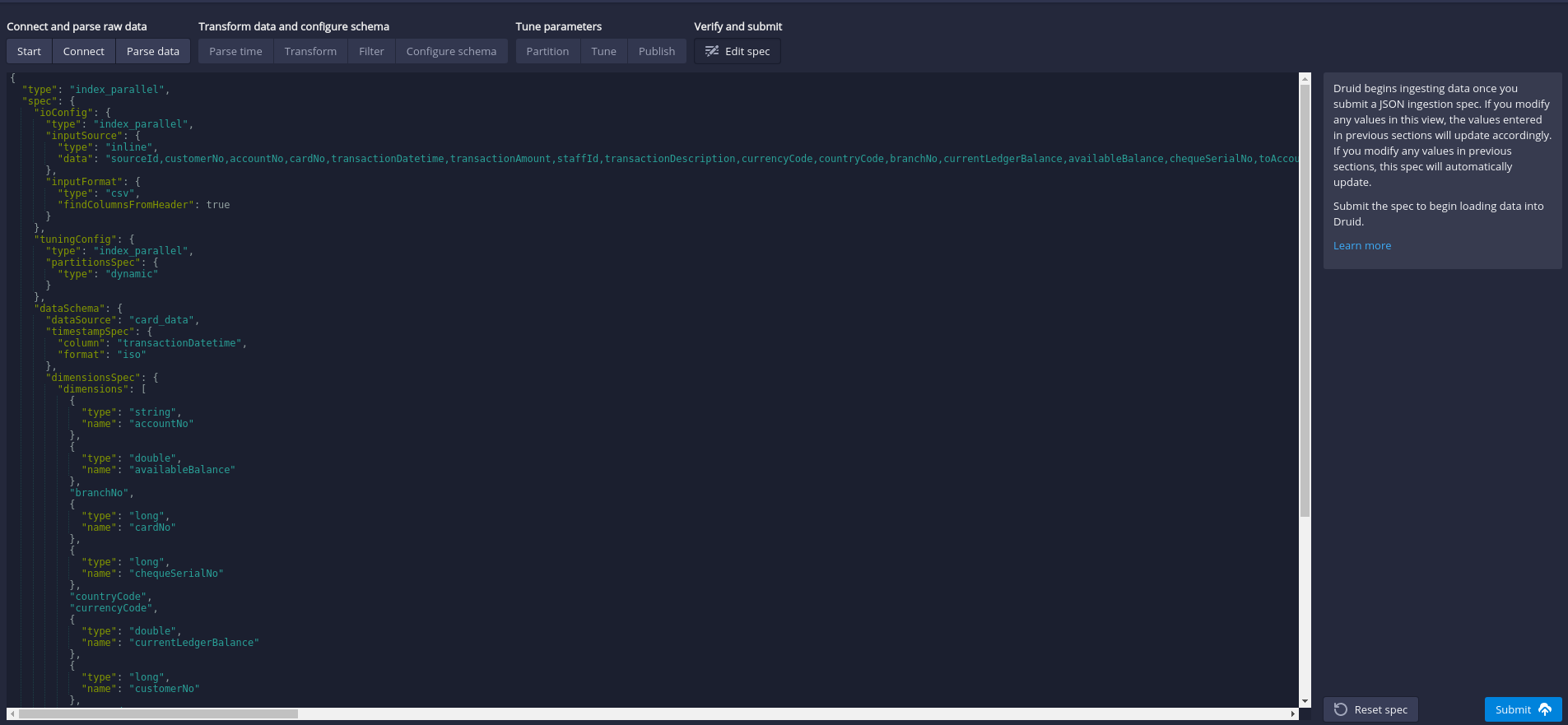
I have prepared a Druid spec file that load data form inline data. Thus we can directly click on the last step
Edit Spec. -
Copy and paste the json content from here and hit “Submit”.
-
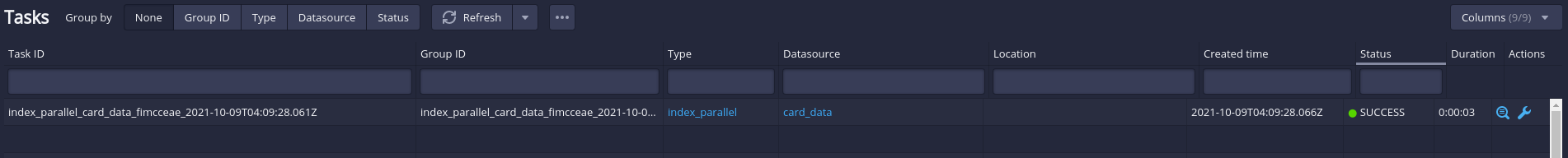
To check the data loading progress, click “Ingestion” from the menu .
-
Once the data ingestion is done. Click “Datasource” from the menu to check the data availability.
-
Done.
REST API
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
## download the json spec file
curl https://gist.githubusercontent.com/lcr95/5da2850c23650448256bce18d3b4b321/raw/0036101347bece53e1b68206f9be0943726fcccb/card_data_spec.json > card_data_spec.json
## submit task to druid
curl --location --request POST \
'http://localhost:8888/druid/indexer/v1/task' -d @card_data_spec.json \
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
Conclusion
In this blog post, we learned how to setup Apache Druid in local and Kubernetes environment, and loading data into Apache Druid.
Reference
- Design - link
- Accessing data using Apache Druid - link
- Druid Operator - link
- Metadata Storage - link